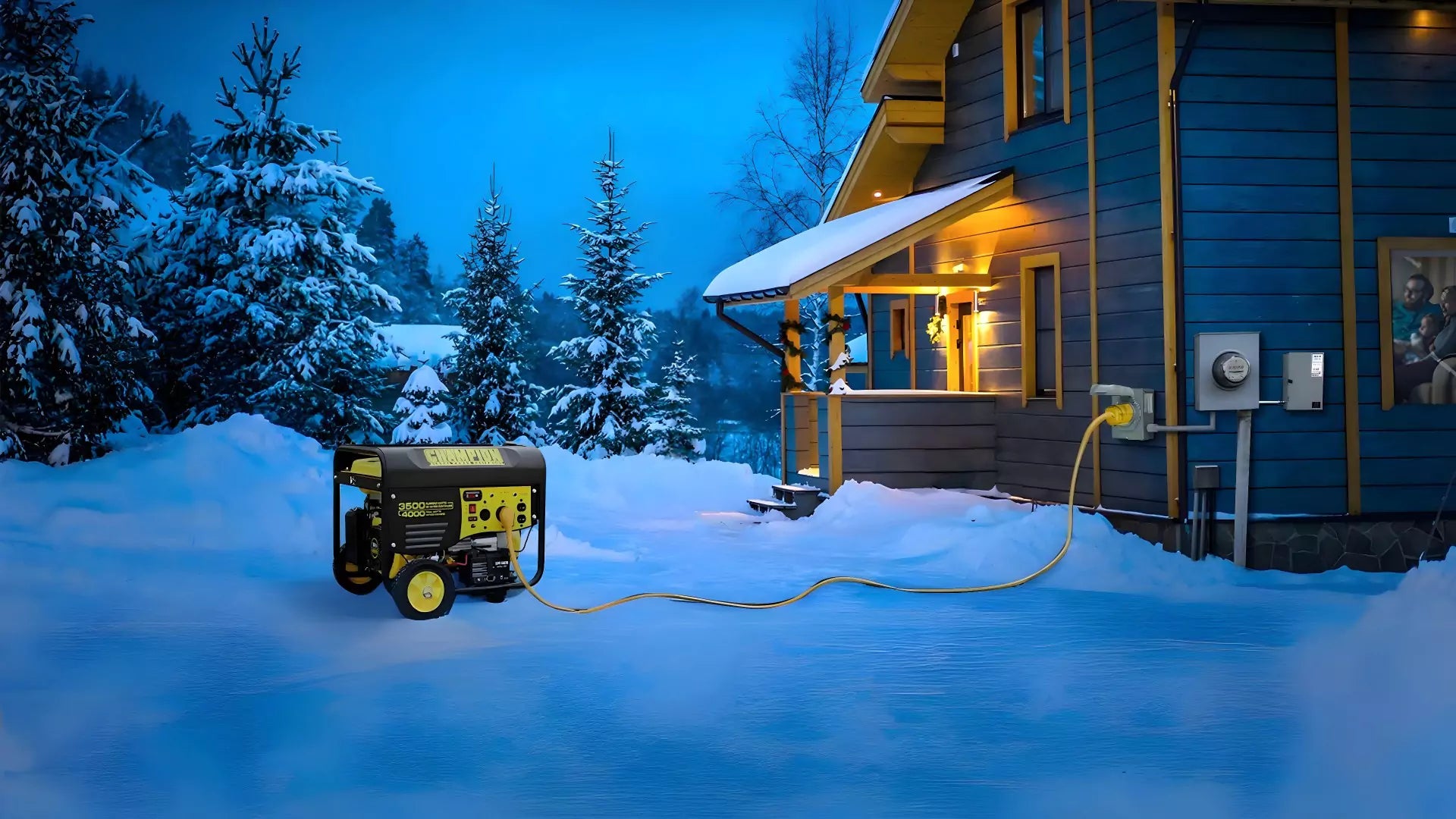
Power outages can strike at any moment, leaving families in the dark and potentially compromising safety and comfort. That's where a well-installed generator comes into play.
However, connecting a generator to a home isn't as simple as plugging in an extension cord. The process requires careful planning, precise equipment selection, and meticulous installation to ensure both effectiveness and safety. Whether you're facing a severe storm, experiencing infrastructure failures, or simply seeking a reliable backup power solution, understanding how to properly connect your generator to your home's electrical system is crucial.
This article will guide you through the process of hooking up your generator and power inlet box at home, ensuring you have the knowledge and tools needed for a smooth setup.

What Should You Know About the Home Generator
Portable and Standby Generator
Home generators come in a variety of sizes and types, designed to provide backup power during outages or to supplement energy needs for outdoor activities. While high-capacity power station systems are gradually replacing fuel generators, fuel generators remain indispensable in certain specific scenarios. Therefore, this article will primarily focus on home fuel generators. They can be broadly categorized into two types: portable and standby.
Portable generators
- They are versatile and can be easily moved to different locations, making them ideal for temporary or occasional power needs, such as camping, tailgating, or providing backup power during brief outages.
- Portable generators typically offer a range from 2,500 to 15,000 watts, providing sufficient power for essential appliances like refrigerators, lights, and small electronics. Smaller generators (2,500 - 3,000 watts) are ideal for outdoor activities such as camping or powering tools on job sites. Larger portable generators (7,500 - 15,000 watts) can handle most household appliances during power outages caused by storms. While they offer flexibility, portable generators require manual setup during power outages, making them best suited for emergency use.

Standby generators
- On the other hand, standby generators are permanently installed and automatically activated during power outages, eliminating the need for manual intervention. Directly connected to your home's electrical system, these generators seamlessly transition between utility power and generator power.
- With a higher power output, standby generators typically offer ranging from 10,000 to 25,000 watts, standby generators can power most household appliances, including air conditioners, refrigerators, and heating systems. While they are more expensive than portable generators, they provide superior reliability and peace of mind.

Understanding the intended use of your generator is paramount. It's not merely about having a power source, it's about having the right power source for your specific requirements. The key to selecting the appropriate generator lies in its intended use and the electrical load it will support.
For instance, if you frequently work outdoors or need to power equipment in off-grid locations, a portable generator is an excellent choice.
Conversely, if you reside in a region prone to severe weather and frequent power outages, a standby generator might be a better option.
When planning to power essential appliances like refrigerators, heaters, or televisions at home, it's crucial to ensure your generator can handle the load.
Key Components of Generators
General generators typically consist of three main components: an engine, an alternator, and a control panel. The engine, the heart of the generator, converts fuel into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then transformed into electrical energy by the alternator, a complex system of windings and magnets. The control panel, acting as the generator's brain, oversees the entire process, regulating voltage output and monitoring system health.
Understanding generator output ratings is crucial. Here are some key terms:
- Watts: A measure of electrical power. It indicates how much electricity the generator can produce.
- Amps: A measure of electrical current. It helps determine how much power can be drawn from the generator.
- Volts: A measure of electrical potential. Most household appliances operate at 120V or 240V.
| Term |
Definition |
Practical Example |
| Watts |
Measure of total power output |
Electricity the appliance can produce |
| Amps |
Electrical current strength |
Circuit load capacity |
| Volts |
Electrical pressure |
Standard home voltage (120V / 240V) |
How to Measure the Power Output of a Generator Charging Your House?
To measure the power output of a generator charging your home, you'll need to calculate the total wattage of all the electrical devices you're running.
Here's how to do it:
-
Find the wattage of each device: Look for a label on the bottom, back, or inside of the device. This label typically lists the device's wattage.
-
Consider different operating modes: The actual power consumption can vary depending on the settings. For instance, a TV on a higher brightness setting will consume more power than one on a lower setting.
-
Calculate total wattage: Use the formula: Watts = Volts x Amps. For example, if your devices operate at 120 volts and draw a total of 20 amps, your total wattage would be 120V x 20A = 2400 watts.
To ensure safe and efficient operation, utilize high-quality, heavy-duty extension cords designed for outdoor use. Before connecting the cords to your generator, conduct a thorough inspection to identify any signs of damage. In the next section, I'll guide you through how to select the right generator power kit to ensure your home always has power.
How to Choose the Right Generator Hook-Up Kit?
Generator Cords
30 Amp or 50 Amp
The key to selecting the correct generator cord lies in matching its amperage rating to your generator's outlet, For example, a generator with a 50-amp outlet should use a 50-amp extension cord, and a generator with a 30-amp outlet should use a 30-amp extension cord.
The 30-amp cord is suitable for generators with a maximum output of around 3,600 watts (30A x 120V = 3600W), ideal for RVs, camping, or small home backups. For larger RVs, construction sites, or whole-house backup power, a 50-amp cord is necessary, as it can handle generators with a maximum output of around 12,000 watts (50A x 240V = 12000W).
When purchasing a generator cord, consider factors like wire gauge, length, and outdoor rating. Additionally, ensure that the cord's plug and receptacle match your generator's outlets.
Remember, it's crucial to consult your generator's manual for specific recommendations and safety guidelines. By selecting the right generator cord, you can guarantee the safe and efficient operation of your generator.
3 Prong vs. 4 Prong
When selecting a generator cord, pay close attention to the plug type.
30-amp generators typically come with either a 3-prong or 4-prong plug. A 3-prong plug is designed for 120-volt power and contains hot, neutral, and ground three wires. It is suitable for powering smaller appliances and devices like lights, fans, and small electronics.
A 4-prong plug, On the other hand, a 4-prong generator cord can handle both 120 and 240 volts, it contains two hot, one neutral, and one ground wires. Making it ideal for powering larger appliances like air conditioners and water heaters.
Remember to choose a generator cord that matches the configuration of your generator and the specific power requirements of your appliances.

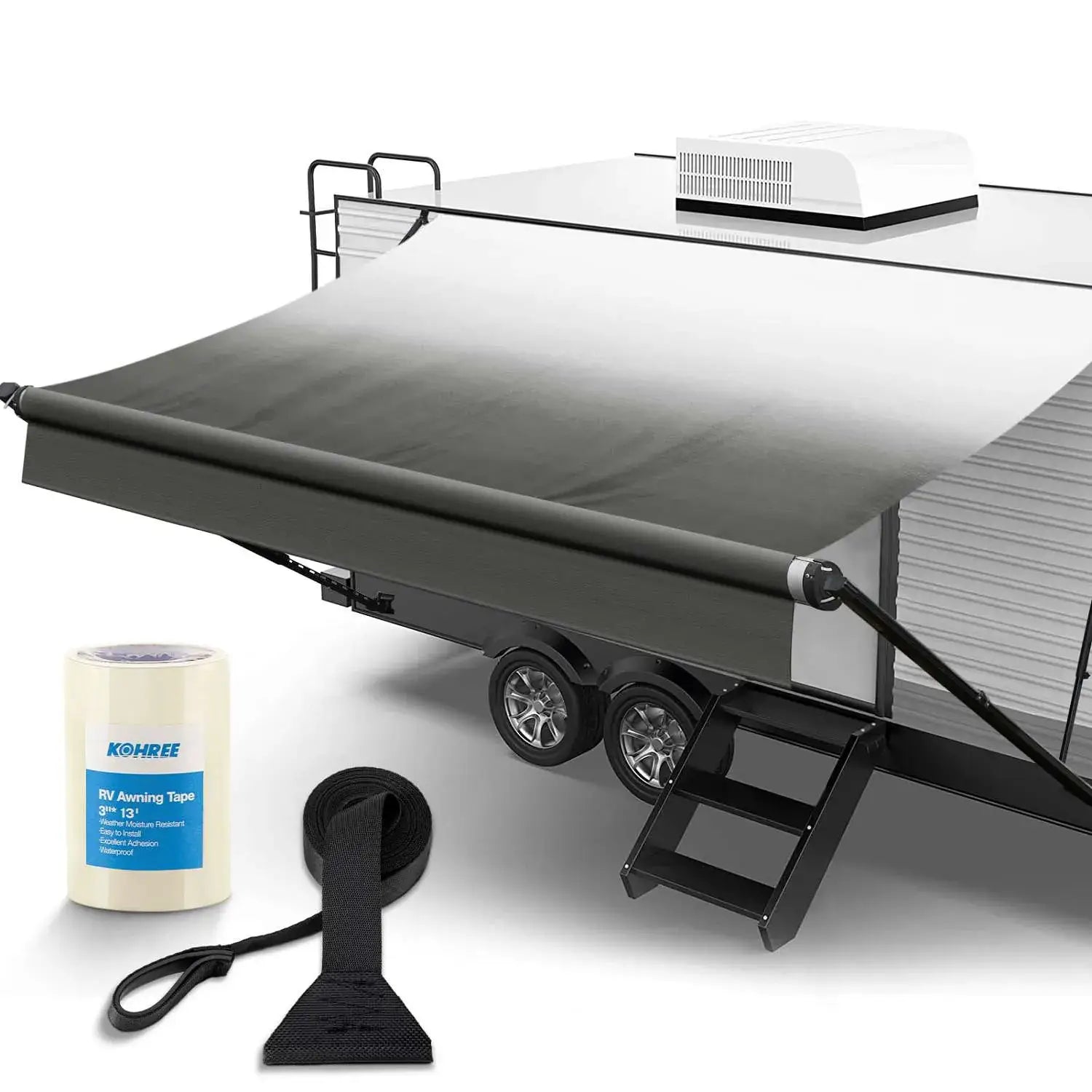
Appropriate Cord Length to Power Home
For optimal performance and safety, choose a generator cord length between 25 and 50 feet for most residential setups. Avoid excessively long cords, as they can lead to significant voltage drop and potential hazards. In colder climates, a more flexible cord is recommended to withstand lower temperatures.
Wire Gauge Requirements
A thicker gauge (lower AWG number) ensures efficient power delivery, while a shorter cord minimizes voltage drop. For example, a 10-gauge wire is suitable for 30 amps, while a 6-gauge wire is needed for 50 amps. Always choose a heavy-duty outdoor cord to withstand harsh weather conditions.

Transfer Switch
Can I Power My House with Just a Generator?
Without a transfer switch, you'll need to manually connect extension cords to individual appliances, which is inconvenient and limits your control over which appliances are powered, potentially overloading the generator.
A transfer switch is an essential component when connecting a generator to your home's electrical system. It automatically switches your home's power source from the utility company to your generator during a power outage, and back again once utility power is restored.
Although the process is automated, you'll need to take an initial step. Ensure the transfer switch is turned on. When a power outage hits, it will automatically switch to the generator.
This not only ensures a seamless transition but also prevents backfeeding, a dangerous condition that can harm utility workers and damage your generator. By installing a transfer switch, you can safely and efficiently power your home during outages.

Factors to Consider When Selecting a Transfer Switch
-
Amperage Rating: The amperage rating of the transfer switch should match or exceed the output capacity of your generator. This ensures that your generator can safely power the connected circuits without risking overload.
-
Number of Circuits: Assess how many circuits you wish to power during an outage. Select a transfer switch that has enough circuits to accommodate your essential appliances and systems.
-
Automatic vs. Manual: Automatic transfer switches (ATS) automatically alternate your home's power source between utility power and generator power, ensuring seamless operation during outages. Manual transfer switches require manual intervention to switch between power sources. While generally less expensive, they necessitate your presence to initiate the transfer.
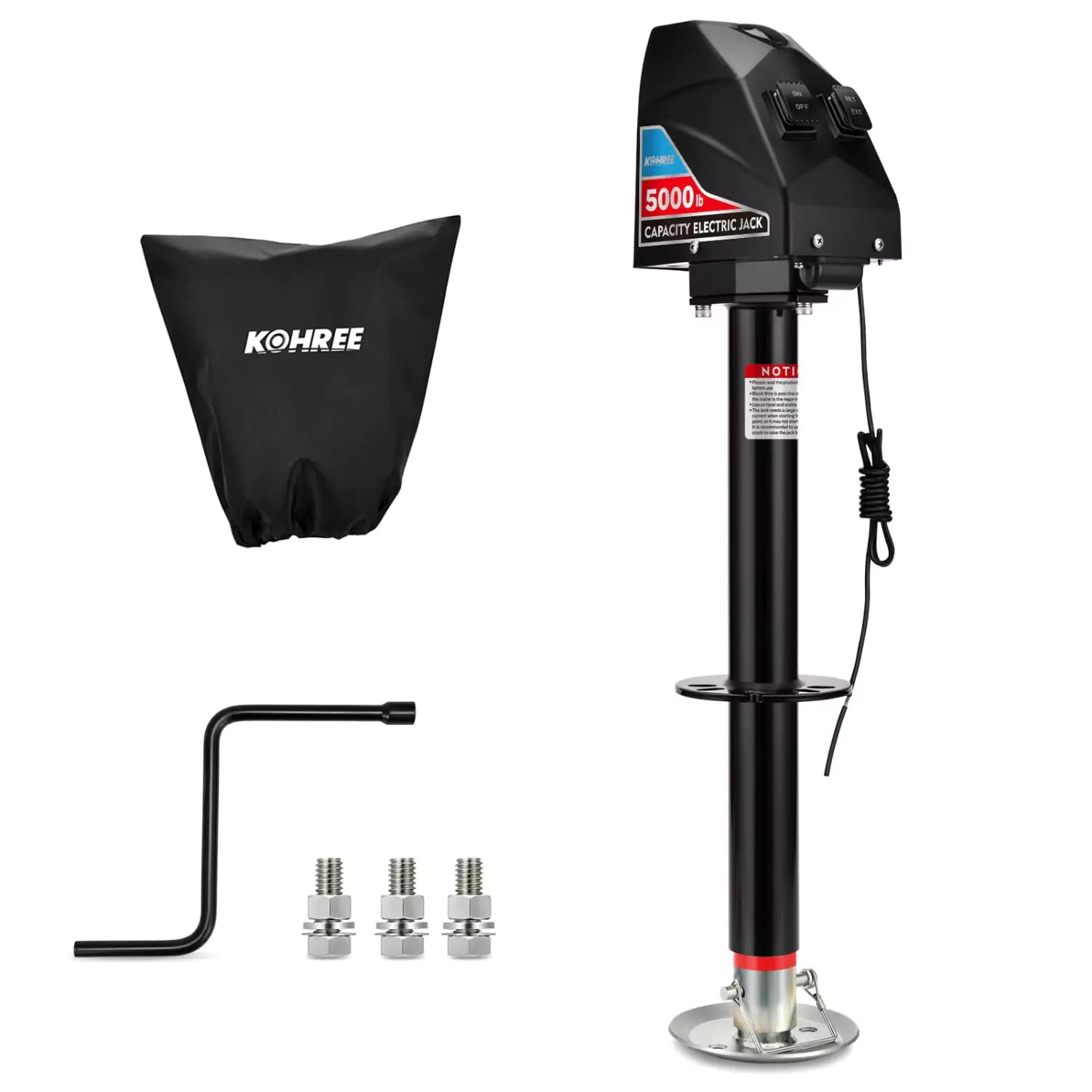
Power Inlet Box
Purpose and Considerations Factors of Inlet Box
The power inlet box serves as a crucial connection point between your generator and your home's electrical system. It ensures a safe and efficient transfer of power during outages. When selecting and installing a power inlet box, consider factors such as compatibility with your generator's cord, appropriate electrical rating, and adequate weatherproofing.

What is the Difference Between Transfer Switch and Inlet Box?
A transfer switch can connect both the utility power and the generator power simultaneously. When you turn on the switch, it automatically switches the power source during an outage, eliminating the hassle of manually connecting the generator to the power inlet box.
A power inlet box is a basic connection point that allows you to manually connect a portable generator to your home's electrical system. It provides a weatherproof outlet for the generator cord, making it a simple and cost-effective solution for temporary backup power. However, it lacks the automatic switching capabilities of a transfer switch, requiring manual intervention during power outages. While suitable for occasional use, a power inlet box may not be ideal for extended power outages or critical applications.

How to Choose Generator Power Inlet Box?
-
Compatibility with Generator: Ensure the inlet box is compatible with your generator's output voltage and amperage. Check the generator's specifications and match them with the inlet box ratings. For most residential applications, a 30-amp or 50-amp inlet box is sufficient.
-
NEMA Rating: Look for the NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) rating of the inlet box. For outdoor use, a NEMA 3R or higher rating is recommended to protect against rain and moisture.
-
Installation Location: Choose a location for the inlet box that is easily accessible and away from potential hazards. It should be mounted securely and within reach of your generator.
-
Ease of Use: When selecting a power inlet box, prioritize those equipped with a weatherproof cover and pre-drilled holes. The weatherproof cover ensures a reliable power supply even in harsh weather conditions, while the pre-drilled holes simplify the installation of power cables. Some inlet boxes feature twist-lock connectors, while others use standard plugs. Ensure that the connector type matches your generator's output.
How to Connect Generator With Inlet Box to Power Your Home?
Want to power your home during a blackout? Installing a generator inlet box is a great idea, but don't worry if you're not an electrician. I'll walk you through the steps of safely connecting your generator to your home. Here is the comprehensive guide to safely connecting a generator to your home's electrical system using an inlet box:
-
Install the Inlet Box:
Choose the right box: Select a waterproof inlet box rated for your generator's amperage (usually 30A or 50A).
Mounting: Install the box securely on an exterior wall near your electrical panel, keeping it sheltered from the weather.
Cable entry: Drill a hole for the generator cord, feed the cable through, and seal the hole with waterproof sealant.
-
Measure and Select the Generator Cord:
Measure the distance: Measure the distance between the inlet box and the generator's location. Ensure it's at least 20 feet away from doors and windows to prevent carbon monoxide buildup.
Choose the correct cord: Buy a heavy-duty, outdoor-rated generator cord with the appropriate AWG size to handle your generator's amperage safely.
-
Wire Inside the Electrical Panel:
Safety first: Turn off the main power to your home.
Connect the wires: Wire the inlet box cable to a matching double-pole breaker in your electrical panel. Connect the ground wire to the ground bus bar, the neutral wire to the neutral bus bar, and the hot wires to the breaker terminals.
Professional help: If you're unsure about electrical work, consult a qualified electrician.
-
Install a Circuit Breaker (Optional):
For higher power: If you need to use more than 50 amps, install a circuit breaker to control power and protect against surges.
Connect the wires: Connect the neutral and ground wires to their respective bus bars. Connect the black and red wires from the cable to the bottom of the circuit breaker and tighten them.
Install the breaker: Mount the circuit breaker onto the bracket in your electrical panel.
-
Install an Interlock Kit:
Prevent back feed: Install an interlock kit on your main breaker to prevent power from flowing back to the utility grid.
Follow instructions: Follow the manufacturer's instructions for installing the interlock kit.
-
Connect the Generator Cord:
Plug one end of the generator cord into the outlet on your generator then plug the other end of the cord into the inlet box receptacle.
-
Proper Cable Management:
Avoid hazards: Route the cord along walls or use cable ramps to protect it from foot traffic and vehicles. Avoid running the cord across walkways or under doors.
-
Power Up Safely:
Turn off appliances: Turn off or unplug non-essential appliances and electronics.
Start the generator: Start the generator and let it stabilize.
Turn on the breaker: Flip on the double-pole breaker in your electrical panel to supply power from the generator.
Important Note: Always consult local electrical codes and follow safety precautions when working with electricity.
Safety Precautions When Using Generators
-
Ventilation is Key: Make sure to always use your generator outside where there's plenty of air. Generators make carbon monoxide, a gas that can make it hard to breathe and even knock you out. So, never run it in places like garages or basements, and keep it away from windows and doors.
-
Carbon Monoxide Prevention: Install carbon monoxide detectors in your home, especially near sleeping areas. Regularly check and replace the batteries in these detectors to ensure their proper functioning. This proactive measure will help safeguard your family from the dangers of carbon monoxide poisoning.
-
Essential Safety Measures: Never refuel a hot generator. Always allow it to cool down completely before adding fuel. Keep the generator dry and avoid operating it in wet conditions. When using extension cords, utilize heavy-duty models specifically designed for outdoor use. Ensure the extension cord's amperage rating is sufficient to handle the connected appliances safely.
-
Generator Cord Safety: Before each use, thoroughly inspect the generator cord for any signs of damage, including cuts, cracks, or exposed wires. Avoid overloading the generator or the extension cord, as this can lead to overheating, damage, and an increased risk of fire. To prevent tripping hazards, route the generator cord away from walkways and driveways.
-
Grounding: Ensure the generator is properly grounded to prevent electrical shocks.
Prepare in Advance to Prevent Power Outages
Generator Cord and Inlet Box Kit
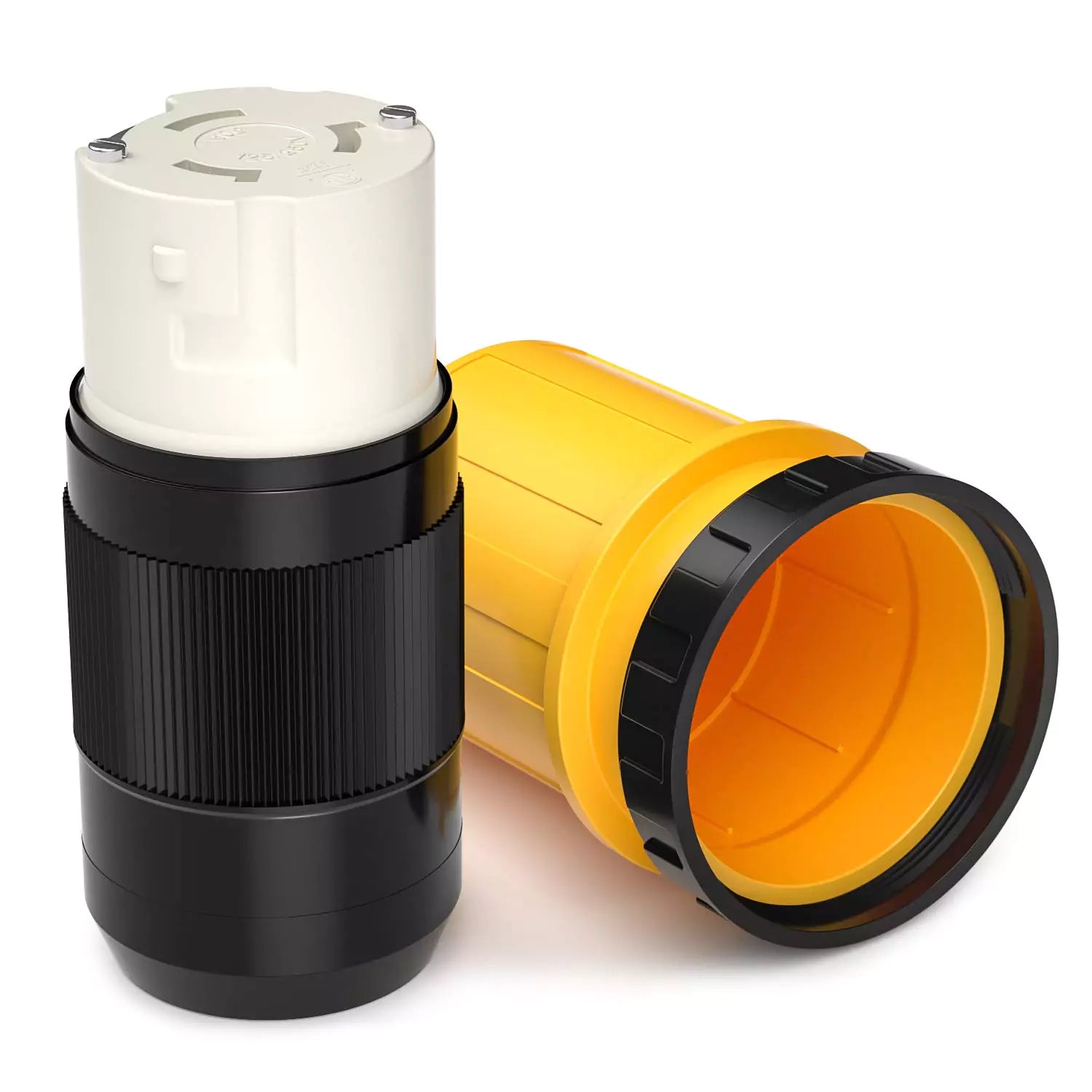
30 Amp Generator Cord: Power Your Essentials with Ease
Experience the peace of mind that comes with reliable backup power. Our 30 amp generator cord and inlet box kit provides everything you need to connect your generator safely and efficiently.
Heavy-Duty Performance: This 25-foot cord, built with 4 x 10 AWG copper wire, features a male NEMA L14-30P plug and a female NEMA L14-30R plug. It delivers up to 7500 watts and 125V/250V of power to essential appliances during outages.

Easy Installation: The included pre-drilled power inlet box simplifies installation, while the twist-lock connector ensures a secure and reliable connection.

Built to Last: Weatherproof construction and ETL safety certifications provide peace of mind, knowing your equipment is protected in any condition.

Complete Package: Includes everything you need: cord, inlet box, cable organizer, and user manual for a hassle-free setup.

Don't be caught off guard by unexpected power outages. Invest in our 30 amp generator cord kit and ensure your home stays powered when you need it most.
50 Amp Generator Cord: Power Your Entire Home
Need to power high-demand appliances like central air conditioning or well pumps? Our 50 amp generator cord and inlet box kit delivers the power you need.
High-Capacity Power: This 15-foot cord, constructed with 6 AWG + 3 x 8 AWG copper wire, is equipped with a male NEMA 14-50P plug and a female NEMA SS2-50R plug. It provides up to 12,500 watts and 125V/250V of power for demanding applications.

Easy and Safe Installation: The pre-drilled inlet box and twist-lock connector ensure a quick and secure setup, while ETL safety certifications provide peace of mind.

Weatherproof and Durable: Designed for both indoor and outdoor use, this home power kit features weatherproof construction and a heavy-duty PVC sheath.

Complete Solution: Includes everything you need: cord, inlet box, cable organizer, and user manual for a seamless and convenient setup.

Experience the peace of mind that comes with reliable backup power for your entire home. Choose our 50 amp generator cord and power inlet box kit and stay prepared for any power outage.
Transfer Switch
15 Amp Generator Transfer Switch: Meets Your Essential Power Needs
Experience the peace of mind that comes with reliable backup power. Our 15 amp generator transfer switch provides a safe and easy way to connect your generator during power outages.
Safe and Reliable: ETL-listed and designed for 1875W, this transfer switch ensures safe operation with compatible 15 amp 3 prong NEMA 5-15P generators.

Easy to Use: The green power indicator light provides clear visibility, especially in low-light conditions.

Easy Installation: The removable front panel and multiple connection options facilitate quick and easy installation.

Built to Last: Constructed from durable steel with a corrosion-resistant finish, this transfer switch is designed to withstand bad weather.
Don't let power outages disrupt your life. Invest in our 15 amp generator transfer switch and ensure your essential appliances stay powered during emergencies.
20 Amp Generator Transfer Switch: Power Your Home with Confidence
Upgrade your home's power resilience with our 20 amp generator transfer switch. This reliable and easy-to-use switch provides seamless power transitions during outages.
Powerful and Reliable: Designed for 20 amp 3 prong NEMA 5-20P generators, this ETL-listed switch delivers reliable power to your essential appliances.

Easy Installation: Prewired with a cord and featuring a removable side panel, installation is quick and hassle-free. Additionally, it includes a prewired circuit breaker, making installation quick and straightforward.

Durable and Weather-Resistant: Built from robust steel with a weather-resistant coating, this transfer switch is designed to withstand rain and UV exposure.

Versatile Applications: Ideal for powering a wide range of appliances, including furnaces, heating systems, lights, and refrigerators.

Experience the peace of mind that remaining powered during power outages, keeps your home or business running smoothly. Choose our 20 amp generator transfer switch and ensure your family stays comfortable and safe.
Conclusion
Connecting a generator to your home is more than a technical task about ensuring your family's safety, comfort, and resilience during unexpected power disruptions. By understanding the components involved, choosing the right equipment, and following safety precautions, you can ensure a safe and effective setup. Whether you're preparing for emergencies or enhancing your outdoor experiences, following these comprehensive guidelines, you'll create a robust, reliable home power backup system. For added safety and durability, consider investing in a high-quality generator kit. It will provide reliable power and protect you from potential hazards.